Quality of Tuberculosis Services Assessments
According to the 2018 Global Tuberculosis Report released by the World Health Organization (WHO), tuberculosis (TB) is the tenth leading cause of death and is the leading cause of death from a single infectious agent.
Studies show that good quality of care in TB services helps patients and their families address their health needs safely and effectively. Therefore, to enhance TB service use, there is a need to assess and improve the quality of TB services. MEASURE Evaluation, funded by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), initiated a series of Quality of TB Services Assessments (QTSAs) to evaluate the quality of TB services in randomly selected health facilities in a number of priority TB countries. The QTSA portfolio was transferred to the TB DIAH project, which will extend assessments to more high-burden TB countries in Africa, Asia, and Europe.
The purpose of the QTSAs is to identify where services were of high quality, where there were gaps, and ensure that TB patients were receiving the care that they deserve. The QTSAs assess three domains of quality of care: the structure of the health facility, the service delivery process, and the outcomes of service delivery.
Global QTSA Toolkit
This Global Toolkit (comprised of an Implementation Guide, Tools, and supplemental COVID-19 modules) presents detailed information and step-by-step guidelines on how to conduct QTSAs in other settings, and provides a generic version of the QTSA tools and other documents useful for conducting a QTSA.
Country QTSAs
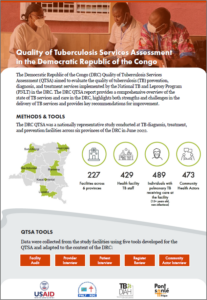
Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)
Vietnam
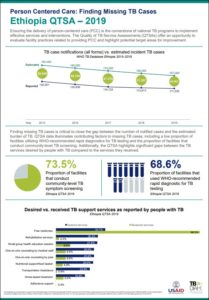
Ethiopia
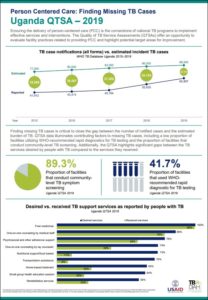
Uganda
A comparison of survey results to evaluate the availability, readiness, and quality of the Uganda tuberculosis diagnosis network was published in 2021.
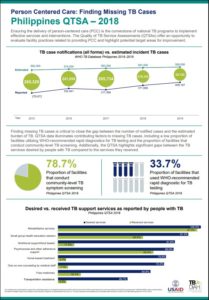
Philippines
Nigeria
Related Content
Comparison of TB Services Available and TB Services Received in Two East African Countries
Are People with TB Receiving Person-Centered Care? A Multi-country Comparison